The UK hospitality sector looks set to be the most affected in terms of economic growth and employment rate after Brexit. BSc Financial Economics student Guglielmo Polizzotto explores where the sector stands now.
According to the Office for National Statistics (ONS), the number of people in work in the UK is over 30 million, with 5.44% of those in hospitality. Between 2016 and 2019, the number of people in work grew by 3.31%, but in hospitality the proportion of workers shrank by 0.04%. In Figure 1, we can appreciate that the difference between hospitality and other industries has been minimal in terms of numbers of employees. To have a better understanding, a look to the employment vacancies is needed.
A 2017 study by People 1st established that strict government conditions of employment for migrants could be the reason why many restaurants and hotels are struggling to fill their vacancies. The UK government asks for certain prerequisites to grant EU migrants access to employment, such as a pre-existing offer of work from the Home Office and a salary of above £25,600.
An average hospitality worker’s salary stands between £17,000 and £21,000, which makes it difficult for any EU worker who would like to work in the UK. So why could this be an issue for the hospitality industry?
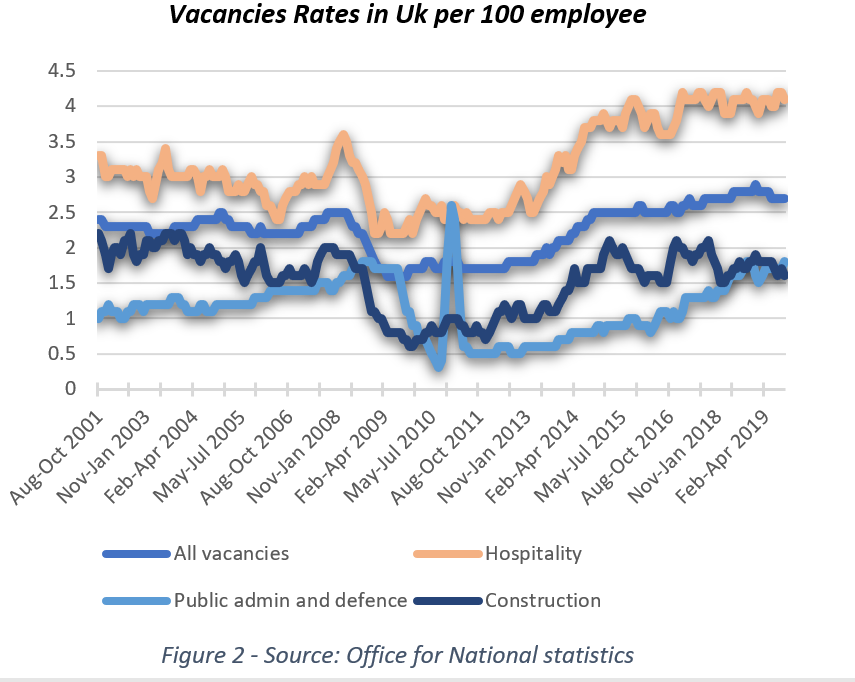
The hospitality sector has the highest vacancy rate compared to other industries in the UK, reaching a peak of four vacancies per 100 people in the past five years. One of the reasons behind these high vacancy rates is that certain positions are considered hard to fill.
Over the last few years, the UK has faced a demographic change, which has seen fewer young people join the labour market and caused a shrink in the pool from which any restaurant or business in the hospitality sector was filling certain positions. Migrants were the solution to this problem; many seasonal or long-term workers are employed to cover those positions which could not be filled by the local workforce.
EU workers have a great impact on those positions considered hard to fill. Immigrants make up 20% of the hospitality workforce and about 70% of these come from EU countries. In a countr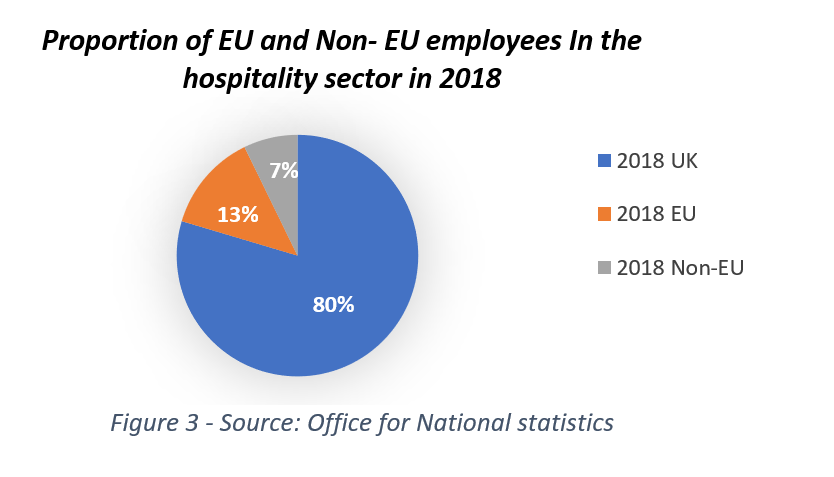 y with a population of over 65 million, it feels absurd that a few hundred thousand fewer workers would create such a problem for the UK labour market. In fact, the issue is more localized than it seems.
y with a population of over 65 million, it feels absurd that a few hundred thousand fewer workers would create such a problem for the UK labour market. In fact, the issue is more localized than it seems.
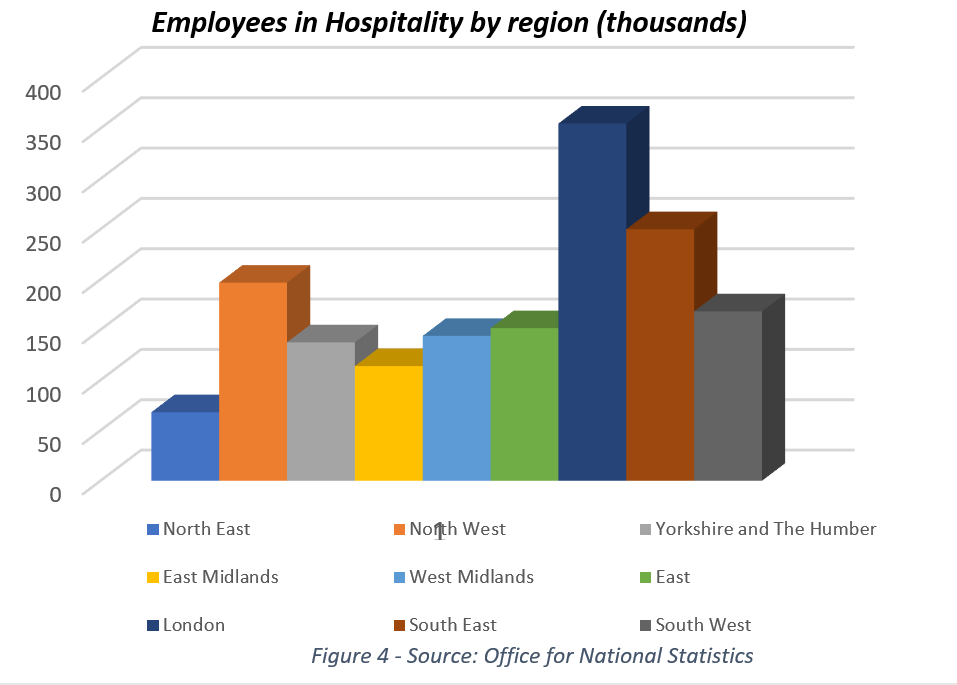 London and the East Midlands have the highest number of employees in hospitality and almost half of them come from EU countries. In a situation where the number of vacancies is rising, but the pool from which businesses fill their positions is shrinking, it will become harder to find employees in certain areas of the UK. Businesses (who can afford it) will be forced to increase salaries to make jobs more appetising or share the tasks between fewer people and leave certain positions unfilled, which can cause distress and decrease the quality of the job done.
London and the East Midlands have the highest number of employees in hospitality and almost half of them come from EU countries. In a situation where the number of vacancies is rising, but the pool from which businesses fill their positions is shrinking, it will become harder to find employees in certain areas of the UK. Businesses (who can afford it) will be forced to increase salaries to make jobs more appetising or share the tasks between fewer people and leave certain positions unfilled, which can cause distress and decrease the quality of the job done.
The time to say goodbye to the EU has come, and while the impact on the workforce looks set to be dramatic, the UK is facing another challenge. With decreasing tourism, and fewer people coming to the UK for work reasons, the labour market is impoverished of its cultural mark that made our beloved country unique.
This blog was originally written as an assignment for the Quantitative Techniques in Applied Economics Module.